If the raster represents a terrain, the valleys become ridges and the ridges - valleys
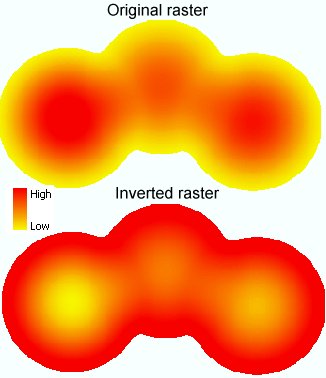 |
Cross sectional profile of the input and output rasters
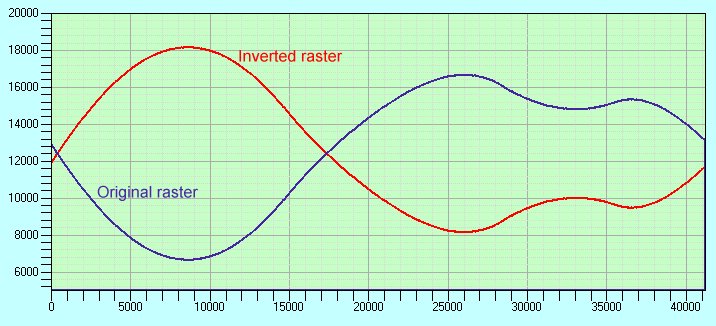 |
Inputs:
- Input raster dataset
- Output raster name and format
Output:
- A floating point raster.
Example:
|
Input raster |
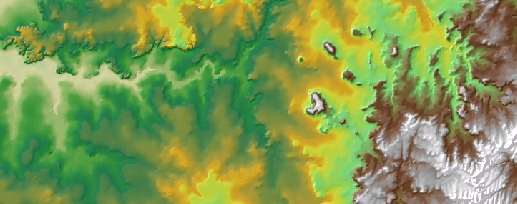 |
|
Inverted raster |
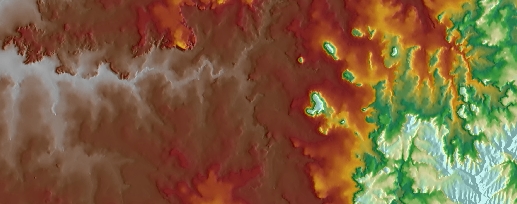 |
Notes:
- Initially the name of the output raster
defines the raster format
- no extension specified - ESRI binary GRID
- .img extension (for example raster1.img) - ERDAS IMAGINE image.
- .tif extension (for example raster1.tif - Tagged Image File Format (TIFF) image.
- The initial output raster format can be changed by selecting the desired output in the dialog.
- Currently only file based rasters are supported. Rasters cannot be stored in a GeoDatabase. After you get the desired result, you can export the raster to a GeoDatabase using the standard ArcGIS tools.
- The input raster must be in a projected coordinate system.
Command line syntax
ETS_GPInvertRaster <Input Raster> <Out Raster>
Parameters
| Expression | Explanation |
|---|---|
| <Input Raster> | A Raster dataset or Raster layer |
| <Out Raster> | A String - the full name of the output raster (A raster with the same full name should not exist). The output raster type depends on the extension of the output file(see Notes above) |
Scripting syntax
ETS_GPPlanCurvature (Input Raster, Out_Raster)
See the explanations above:
<> - required parameter
{} - optional parameter
All ESRI
products mentioned are trademarks of Environmental Systems Research
Institute, Inc.
Copyright: Ianko Tchoukanski